Sometimes runners have a tendency to run and only run. For good reason. Running is fun, endorphins are released and running feels like an efficient use of your exercise time. If you are like me, I love putting races on my schedule to have something to aim for and to give me that extra push when I might otherwise not get out for a run. But to be a complete runner, one should think of running as going hand in hand with strength and stability training. Strength and stability training can be very beneficial to reduce the risk of injury as well as enhance running performance. Runners are often diagnosed with injuries including Achilles tendinopathy, patellofemoral pain syndrome, ITB syndrome, medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints) and hip bursitis. Use of a formal training program has been found to decrease the risk of race related injury among half marathoners. Even elite runners have a strength and stability program built into their regimen.
Balance
What is balance?
Balance is essential to nearly all aspects of life. Sitting upright, standing, walking, running, jumping, and playing sports all require a coordinated effort from your neurological and muscular systems. Good balance is often taken for granted throughout day to day life, but poor balance can significantly hinder your mobility and ability to participate in your desired activities. More importantly, poor balance can lead to falls and injury. Fortunately, balance can be retrained and improved with practice.
Stretching
Everyone knows that stretching is good for you, but most people are wrong in WHY they think it is good for you. As a PT and frequent gym-goer, I often hear that stretching is good because it helps lengthen the muscles. This is completely wrong. I think it is time to debunk some of the myths surrounding stretching. After reading this page, you will have a better understanding of what does and does not happen when you stretch. You might even be able to enlighten those around you in yoga class or at the gym.
Working From Home
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, millions of people are now working from home and needing to get used to a “home office” instead of their normal “in-office” work space. We are so thankful that this is an option for so many people and want to make sure that the home office can be set-up to offer optimal work conditions. Poor ergonomics can make for a miserable work experience and can lead to/exacerbate neck and back pain among other musculoskeletal problems.
Sleep-more in Seattle
Sleep hygiene is a term that is becoming more popular as we learn how important sleep can be for our health. This term encompasses different strategies to establish daily habits that can ultimately increase the quality and quantity of your sleep providing you the necessary rejuvenation after a long day.
● Exercise
● Relax the mind
● Limit alcohol and caffeine
● Set your biological clock
● Set up sleep-friendly environment
● Limit naps and manage restlessness
Adaptation to Load
Have you ever been so sore after a new workout or return to activity that you can barely sit down to use the toilet? This is your body adapting to a new load. This is a fairly simple, but important concept. If your body hasn’t experienced this load ever or in a long time, the chances that you will be sore range from pretty high to certain. Sometimes this scenario leads to 2 days of soreness (DOMS: Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness) and then you return to whatever activity made you sore. Great, your body adapted to the load! On the other side, you find your body was unable to adequately adapt and maybe you cannot return to that activity. Now we have an injury to deal with.
One thing that has been on my mind, and the minds of many other rehab professionals, is...will we see an uptick in injuries for athletes during and after the COVID shutdown? That all depends on whether athletes have been able to maintain their tolerance for the loads that they will be returning to (running, jumping, etc); and/or if they are able to return gradually enough to their respective activities giving their body adequate time to adapt.
Osteoarthritis in My Knee
Knee pain can slow down the best of us but with physical therapy much of the limitations can be improved. Climbing stairs, biking, running, gardening, playing with kids, hiking, and long walks can all be improved with range of motion, balance, and strength. Ask a physical therapist today for more information.
"No I can't, I have a bad knee"
Knee pain can slow down the best of us but with physical therapy much of the limitations can be improved. Climbing stairs, biking, running, gardening, playing with kids, hiking, and long walks can all be improved with range of motion, balance, and strength. Ask a physical therapist today for more information.
ACL Return To Play
Neck Pain
Neck pain and Physical Therapy
If you are having neck pain, physical therapy is often recommended. After
ruling out serious conditions from your doctor, your PT will put together
a treatment program that may consist of:
- Manual therapy: to help with tissue healing and/or restoration of joint
mobility.
- Exercises: to help strengthen your neck and core and improve neutral
postural alignment.
- Pain relief: consisting of appropriate modalities such as ice, heat,
ultrasound, or electric stimulation.
- Patient education: on tips to help reduce stress on your neck in your
work and home environment.
The best new of all is that insurance covers PT sessions! A physical
therapist can work with you and modify your treatment program until you
are healed. Come see a PT today!
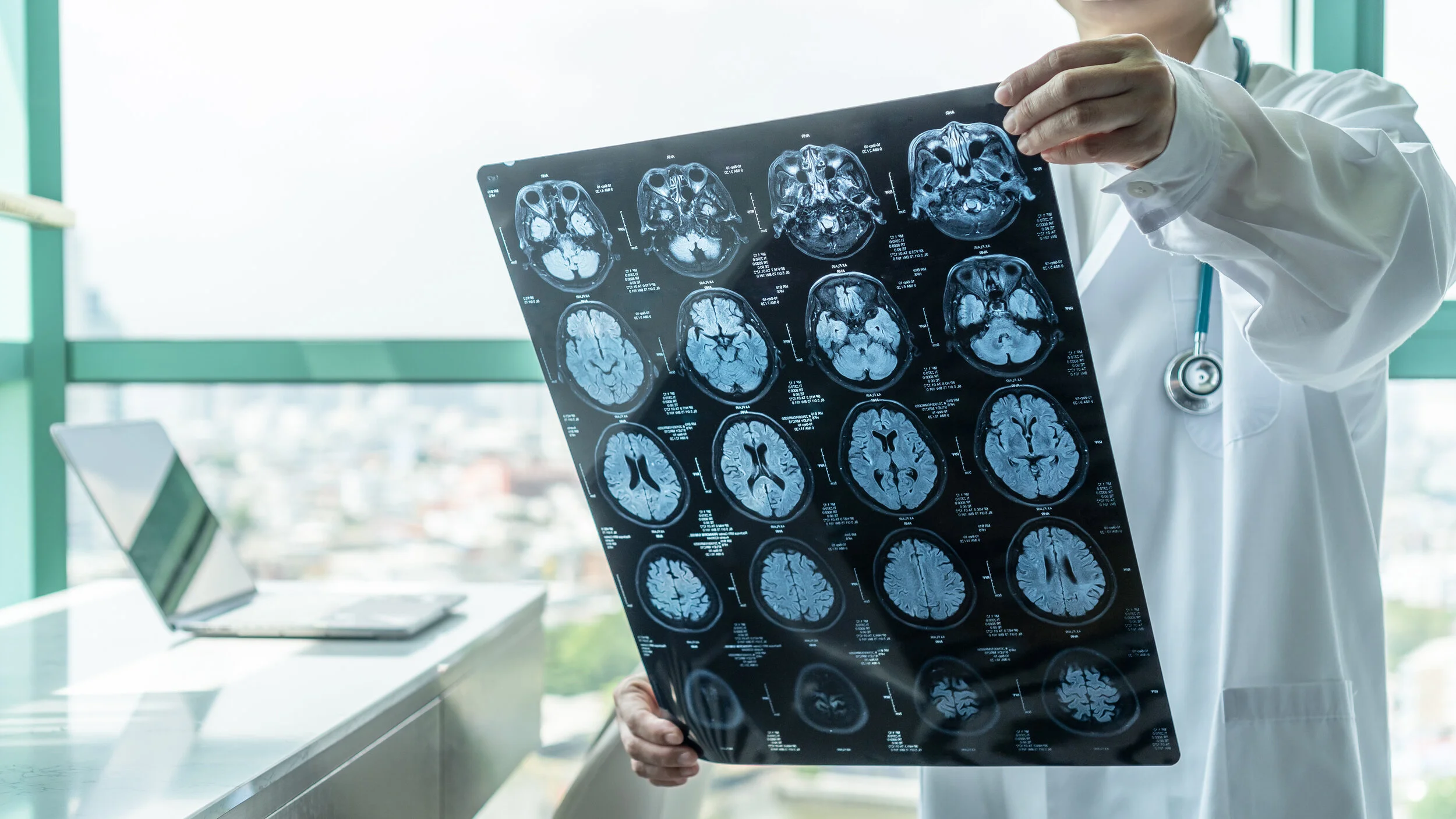
Early Physical Therapy after Concussion
Within the last decade, physical therapist’s role in concussion management has emerged. A landmark research article released in 2018 makes a strong suggestion that physical therapists are great entry points into the medical management of the recently concussed athlete, even within the first week.
Ellis’s research group published their article stating that contact with a physical therapist within the first week after their concussion can be important for athletes. The reasoning stems from the fact that physical therapists can administer and devise a rehabilitation program to help the athlete retain as much of their physiological conditioning during their recovery process. Ellis’s group cites an article that states after a short period of time without any exercise, there are deleterious effects to the athletes physiology and exercise tolerance.1
Neck Pain
Neck pain and Physical Therapy If you are having neck pain, physical therapy is often recommended. After ruling out serious conditions by your physical therapist or your physician, the real work begins.
Your PT will put together a treatment program that may consist of:
Manual therapy: to help with tissue healing and/or restoration of joint mobility.
Exercises: to help strengthen your neck and core to improve neutral postural alignment.
Pain relief: consisting of appropriate modalities such as ice, heat, ultrasound, or electric stimulation.
Patient education: on tips to help reduce stress on your neck in your work and home environment.
When asked about neck pain one of our favorite physiatrists Dr. Gary Chimes, MD stated that, “Neck pain can be one of the most debilitating issues that we see. It can not only effect your physical ability, but also create issues with sleep, mood, concentration, performance, and emotion.”
The best news of all is that insurance covers physical therapy sessions! A physical therapist can work with you and modify your treatment program until your goals are met. Come see a PT today!
Babies & Ergonomics
Best (ergonomic) Ways to Hold and Carry a Baby
In October we welcomed a new team member to our crew, baby Griffin! Having a baby around means a lot of holding and carrying a squirmy ~15 pound active little boy (and other heavy baby gear). While it’s not always possible to think about ergonomics, we thought it’d be helpful to share a few tips regarding this topic to try and protect any new parent’s shoulders, back and hips!
• Each time you carry your baby try to switch sides. This will protect one hip and arm from constantly carrying the load.
• Same goes for loading/unloading the car seat. If the car seat is in the middle seat of the car, try to alternate which side of the car you load and unload from. Also, try to load/unload in two steps instead of trying to maneuver the car seat in and out in one difficult motion.
• When picking up your baby from the floor, bend your knees and lift with your legs instead of from your back. Bring your baby in close to you instead of extending your arms out. This will protect your shoulders and upper back.
• Try to resist the urge to hike your hip and rest your baby on your side – or at least try and limit the amount of time you’re in this position. Over time, this position can lead to malalignment of your pelvis, hips, and back.
• Consider “wearing” your baby in a carrier. There are a lot of great online and in-person resources to learn the best (and safest) techniques.
• If possible, carry the diaper bag “messenger style” with the strap across your body instead of over one shoulder. Better yet, use a backpack diaper bag.
Lastly, let your physical therapist know if you are having trouble with any of these tasks. We can help you figure out the best mechanics for your body.
Rotator Cuff Tears
Why You Need Physical Therapy for Rotator Cuff Tears?
If you’ve never had a rotator cuff tear, chances are good you know someone who has. It’s a common—yet painful—shoulder injury problem affecting millions of patients every year. With proper treatment, however, you can ease pain, keep the injury from getting worse, and heal. More often than not, that treatment includes physical therapy.
The rotator cuff, a group of four tendons that cover the head of the humerus, keeps the arm in the shoulder socket and allows the arm to be lifted and rotated. However, when one or more of the rotator cuff tendons is torn, it sometimes no longer fully attach to the head of the humerus, often resulting in pain and limited mobility.
A Real Pain in the Shoulder
Rotator cuff tears occur either suddenly or gradually. Sudden tears, perhaps caused by falling, tend to result in intense, acute pain as well as a snapping sensation and immediate weakness in the upper arm. Gradual tears, which usually come from overuse, may start with mild pain but can worsen over time. The most common symptoms of rotator cuff tears include:
Pain at rest or at night
Pain when lifting, lowering, or rotating the arm
Weakness in the arm
Crackling sensation in the arm with certain movements
Causes and Treatments
The two main causes of rotator cuff tears are injury and degeneration, and this type of injury tends to become more common with age. A rotator cuff may tear partially or completely. Partial rotator cuff tears can sometimes be treated with rest, anti-inflammatory modalities, and physical therapy.
Full-thickness (complete) rotator cuff tears usually do not heal on their own. When pain and weakness persist, surgeons can repair the rotator cuff. Dr. Samuel Koo from ProOrtho reports “shoulder surgery can now be done arthroscopically, which allows for a quicker recovery and less postoperative pain.”
Arthroscopy is a way of performing common orthopedic procedures through a minimally invasive approach. A small lens, called an arthroscope, is used to visualize the inside of the shoulder. The “scope” gives the surgeon a couple of advantages over open techniques.
First, the shoulder is in a relatively tight space. When open incisions are used, visualization can be difficult simply due to the limitation in where the incision can be placed. Surgeons are often confined to a deep hole in which identification of the tissues can be extremely challenging. The scope, on the other hand, can be placed virtually anywhere allowing easy access to tight spaces using tiny incisions.
Second, anatomic structures in the shoulder are quite small. Modern arthroscopes display images on a LCD monitor in HD quality. Additionally, it magnifies the view so that objects appear bigger than they actually are. This gives the surgeon the feel of using a microscope without actually looking through one!
How Physical Therapy Helps With Rotator Cuff Tears
Although physical therapy alone can’t fully heal rotator cuff tears, it’s often the recommended treatment for them. That’s because the goal of treatment isn’t necessarily to heal the torn tendon; instead, the aim is to ease pain, improve strength, and restore joint shoulder mechanics.
Rotator cuff PT targets the small muscles around the shoulder that tend to be neglected in normal exercise and are thus prone to weakness and breakage. For most patients with rotator cuff tears, these exercises will help relieve the pain and strengthen the shoulder, canceling out the need for surgery. LWPT gives rotator cuff tear patients more one-on-one time with you, so you can quickly start the path to less pain and better mobility.
How Physical Therapy Can Help Those Who Have Sustained a Concussion.
As popularized throughout sports, concussion has been a trending topic throughout all media outlets. In the last decade expert scientists, physicians, and other healthcare providers have strived to address the wave of questions and concerns raised by those affected and their loved ones.
Though most of the literature reviews and studies sports related concussions, I believe much of the information can be applied to the many individuals with general concussions. With winter in full effect, concussions can be caused not only from winter sports, but also from accidents caused by ice (motor vehicle accidents, slip and falls, etc).
This past summer, I attended a Seattle Pediatric Sports Medicine conference that had a panel of healthcare providers who manage patients with sports-related concussions. They discussed the current topics on concussion management and how they approach each case. Most members of the panel were a part of the University of Washington Concussion team.
The University of Washington does a great job in providing information on the background and general symptoms of concussion. You can access their tremendous resource here.
The main points I took from the conference is that current up-to-date acute treatment of concussion does not require the affected individual to sit in a dark room until symptoms to diminish. These individuals don’t require prolonged avoidance of TV or phone screens. Additionally I learned that chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is still in its infant stages of research and scientists are unable to conclude that multiple concussions are the actual causes of CTE. The most important fact I was reminded of was that concussion treatment requires a team approach, which can sometimes include physical therapy.
How Physical Therapists Can Help
According to the most recent consensus statement released by the Concussion in Sport Group in 2016, “Sports related concussions can result in diverse symptoms and problems, and can be associated with concurrent injury to the cervical spine and peripheral vestibular system… the data support interventions including psychological, cervical, and vestibular rehabilitation.”1 You can read more here on the 2016 Berlin Concussion Consensus Statement.
Most concussion symptoms tend to resolve after 2 weeks. However if there are lingering symptoms, seeing a physical therapist may be a great option to help with an individual's recovery. Here is how we can help.
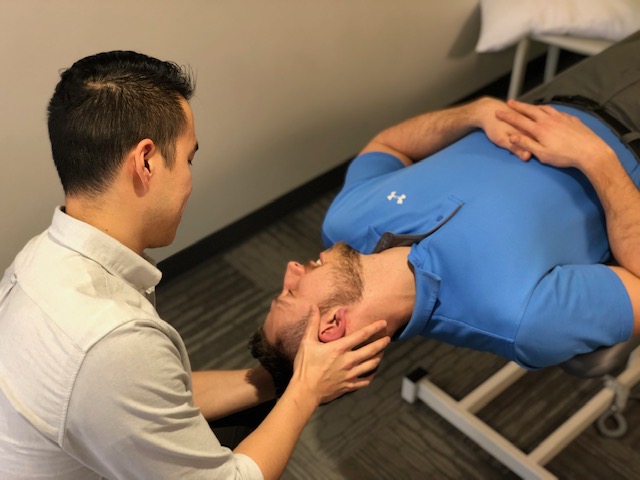
Neck Rehabilitation
Sustaining a concussion can result from multiple types of head trauma. What affects the head likely affects the neck. The body will do everything it can to protect the head and often stiffen your neck. With pain playing the role of your alarm system, it’s with no surprise that the neck becomes extra guarded and irritated when you try to move it. Physical therapists can improve your cervical and thoracic spine mobility and implement strategies and interventions to decrease your discomfort. From manual therapy to progressed therapeutic exercises, PT interventions can help improve neck function.
Vestibular Rehabilitation
Vestibular specialized physical therapists can help those after concussion who continue to feel dizzy or off-balanced. Symptoms may include but are not exclusive to dizziness, vertigo (room spinning), disequilibrium (off balance, nausea), and visual impairment. Seeing a physical therapist who specializes in vestibular rehabilitation can be a valuable member on your team. After a thorough evaluation, they can provide you strategies and exercises to help your vestibular system adapt.2
Benign Paroxysmal Positional vertigo (BPPV) is the most common vestibular pathology that can occur after head trauma. Symptoms include head motion-induced vertigo, normally triggered when rolling in bed or turning the head quickly. This vertigo lasts for seconds, often followed with a fog or lightheadedness lasting for hours afterward. If diagnosed correctly, this can be treated with great success by a trained professional.3 You find more information here.
Lower Limb Injuries Risk Reduction
Though not mentioned in the 2016 Consensus, within the sports concussion literature there has been growing evidence on how concussions may have an influence on future lower limb injuries. What is proposed is that after a concussion, the joints, muscles, and tendons in your legs have an impaired ability to detect where they are in space. Though this may not fall into the category of concussion rehabilitation, orthopedic rehabilitation can help address proprioception and neuromuscular control impairments for athletes who are looking to return to play.4
As for other common symptoms stemming from a concussion, other professionals including neurologists (migraine/headache specialist), neuropsychologists, speech therapists, and vision therapists would be great resources to consult. Ask your concussion management team if physical therapy is right for you and your symptoms and find a local clinic that has a clinician there to help you.
References:
1. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Dvorak J, et al Consensus statement on concussion in sport—the 5th international conference on concussion in sport held in Berlin, October 2016 Br J Sports Med 2017;51:838-847.
2. Gurley JM, Hujsak BD, Kelly JL. Vestibular rehabilitation following mild traumatic brain injury. NeuroRehabilitation. 2013;32(3):519-528. doi:10.3233/NRE-130874.
3. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV). American Physical Therapy Association. https://www.moveforwardpt.com/SymptomsConditionsDetail.aspx?cid=52822493-32f3-4d4c-8c56-8e18c41b2f85. Published September 1, 2015.
4. Kardouni JR, Shing TL, Mckinnon CJ, Scofield DE, Proctor SP. Risk for Lower Extremity Injury After Concussion: A Matched Cohort Study in Soldiers. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 2018;48(7):533-540. doi:10.2519/jospt.2018.8053.
Information provided on lakewashingtonPT.com and all of its web pages is intended for general educational and entertainment purposes and is not intended to be medical advice to you or any other person. You should always consult with your own medical provider about your health and medical questions and never rely on this or any other web site alone to make medical decisions. Never delay seeking medical advice or disregard any medical advice you have received from your provider because of anything you read or hear on this website.
Words Matter
Words Matter:
Language choices made in medicine
Communication between patients and their medical providers plays a large role in a patient’s understanding of their diagnosis and management options. It can drive a patient’s decision to undergo surgery, start PT, or choose no treatment at all. Whether it is your PT or PCP, you are likely being infiltrated by words which may be scary and/or confusing. Some examples might be “disc herniation of L3-5, severe foraminal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, tibiofemoral osteoarthritis, etc, etc.”
Research has shown that when a more medically precise term is used to describe a patient’s condition, they tend to have a stronger preference for choosing more invasive treatment options even if this might not be the best option. Additionally, a person feeling fear or anxiety as a result of such terminology is going to have greater difficulty making informed decisions that let them be an active participant in their care. To keep the story short and sweet, try to not let words scare you. And if you do find yourself scared by your diagnosis and treatment option, ask for an explanation that helps you understand your diagnosis better and that lets you move forward with confidence in whatever treatment option you choose. Chances are your diagnosis may not be as bad as it sounds in words or on the MRI report you receive from your doctor; and it may have several conservative treatment options that would be beneficial. Be an active participant in your care and seek out the answers to the questions you have to ensure you’re getting the best possible treatment for your condition.
Citation: “Words do matter: a systematic review on how different terminology for the same condition influences management preferences”
What is a DPT?
What does DPT mean?
We as physical therapists get a lot of questions regarding the letters after our names. Most commonly, you will see “Mary Jane, PT, DPT” if that person has graduated in the last 10 – 15 years. Breaking that down, “PT” simply indicates the person’s title of Physical Therapist and means that they have passed their national licensure exam to treat patients. “DPT” indicates the degree that person has earned and stands for Doctor of Physical Therapy. If you see “MPT” that person just graduated before the transition to “DPT” and is no less qualified to treat you. The MPT was traditionally 2 years post-baccalaureate whereas the DPT is now 3 years. The next question that inevitably follows is, “Oh! So, you have a PhD?” The answer to that question is “no”, but the semantics of it all can get confusing, so let’s clear that up.
The term “PhD” stands for Doctor of Philosophy and is the highest degree you can achieve in nearly every other discipline except medicine. This is a research degree which focuses on scholarly/professional development. People often go on to teach in their respective area after completing this degree.
A Doctor of Physical Therapy is typically considered a professional or clinical degree. It focuses on the development of skills / knowledge needed to carry out the requirements of their profession. This involves a didactic classroom approach as well as in-clinic experience under the license of supervising practitioners in the field. Also different from a PhD, though similar to the DPT, is a Doctor of Medicine (MD), a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP), and Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degrees. Though these programs differ significantly in length and content of the curriculum, they also do not result in a PhD.
More on Caitlin and her other articles (click here)
PRP
What is a Platelet-Rich Plasma injection?
Background: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection is a medical treatment for orthopedic injuries and conditions. PRP is a form of your own blood that has a high concentration of cells called platelets. Platelets contain substances called growth factors that have the ability to reduce some pain and inflammation and enhance your body’s ability to heal itself. A PRP injection can possibly reduce the need for surgery or procedures for some people.
PRP injections have been used to treat a range of conditions including to treat orthopedic conditions, including osteoarthritis, tendinitis, tendon and ligament tears.
Platelets contain components that can be effective in tissue repair:
Connective tissue growth factor (effective on cartilage, tendons, ligaments, bone growths)
Insulin-like growth factors: IGF-1 and IGF-2 (increase tissue proliferation, decrease inflammation
Vascular endothelial growth factor
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)
Fibroblast growth factor (helps wound healing, aesthetics)
Keratinocyte growth factor (helps wound healing, aesthetics) · Interleukin 8
Transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ)
In my case the PRP was used to treat a moderate medical meniscal tear on my left leg. This was an injury that was at the time of injection 6 months old. I had put myself through a conservative rehab regimen of originally rest, then Range of Motion work, and eventually open & closed chain strength training. A side note which I will cover in another blog are the issues that I had for the previous 6 months in compensating for the tear and pain.
The procedure is relatively quick. From check in to walking out was under 60 min. The pain level was very low in my opinion. The knee capsule does have a fair amount of nervous tissue as the wider gauge needle comes into contact with it but would likely rate this a 4/10 and only for 15-20 seconds….
I will be writing more articles on my progression & protocols that I am developing to better work more efficiently with individuals after PRP has been completed.
There are many Offices where PRP is performed:
(here are a few we work with commonly)
Lake Washington Sport & Spine
ProOrtho: Dr. Camille Clinton, MD
Dr. Ghislaine Robert, MD
UW Medicine: Dr. Rao